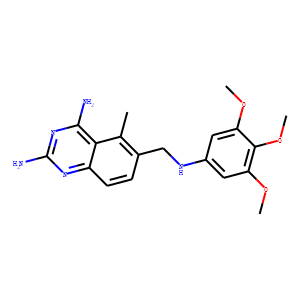
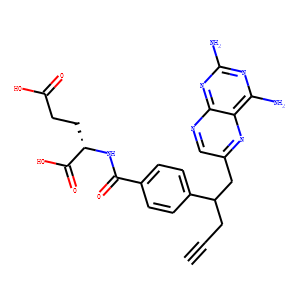
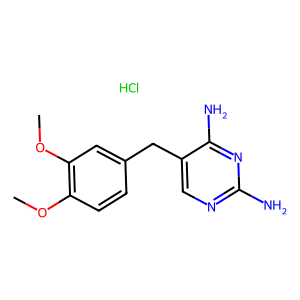
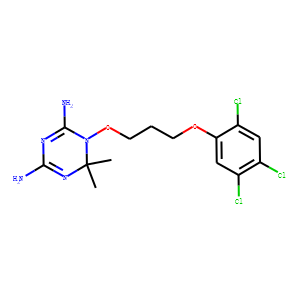
Dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR)
Dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in cellular metabolism by catalyzing the reduction of dihydrofolate to tetrahydrofolate (THF). THF is essential for the synthesis of nucleotides required for DNA and RNA production, making DHFR vital for cell division and growth. Due to its key function in nucleotide synthesis, DHFR is a common target for chemotherapeutic agents. Drugs like methotrexate and trimethoprim inhibit DHFR, thus preventing cell proliferation. These inhibitors are used in the treatment of various cancers, autoimmune disorders, and bacterial infections, exploiting the rapid growth and division rates of cancer cells and bacteria compared to normal cells.