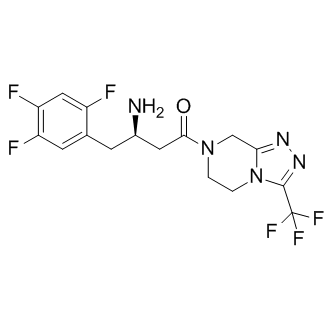
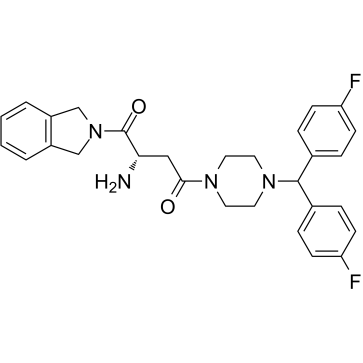
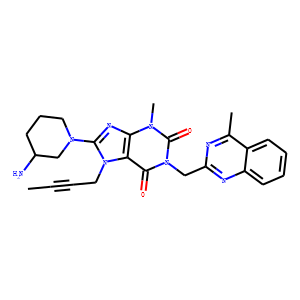
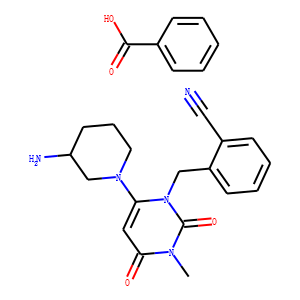
Dipeptidyl Peptidase
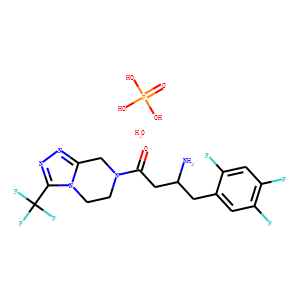
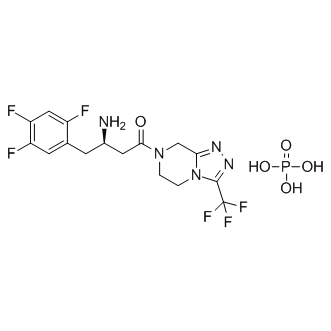
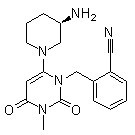
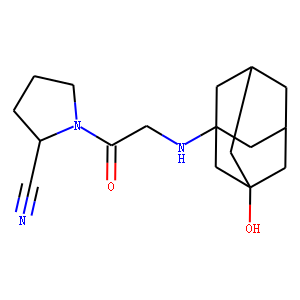
Dipeptidyl peptidase (DPP) enzymes, particularly Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 (DPP-4), play a crucial role in metabolic regulation and immune function. DPP-4 specifically targets and inactivates incretins such as glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), which are hormones that stimulate insulin release in response to meals. By breaking down these incretins, DPP-4 regulates glucose levels in the blood. Given its significant role in glucose homeostasis, DPP-4 is a popular target for diabetes treatment; DPP-4 inhibitors help extend incretin activity, thereby enhancing insulin secretion and lowering blood glucose levels. Additionally, DPP enzymes are involved in the metabolism of many other peptides, affecting various biological processes.