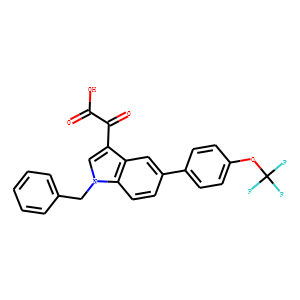
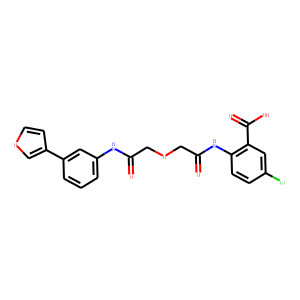
PAI-1
PAI-1 (Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1) is the principal inhibitor of tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) and urokinase (uPA), enzymes that convert plasminogen to plasmin, a major enzyme responsible for clot breakdown. PAI-1 thereby plays a critical role in the regulation of fibrinolysis, the process by which the body breaks down blood clots. Overexpression of PAI-1 can lead to an increased risk of thrombosis because it inhibits clot dissolution, contributing to cardiovascular diseases like heart attacks and strokes. Conversely, low levels of PAI-1 can cause excessive bleeding. PAI-1 levels are influenced by genetics, obesity, and other metabolic factors, making it a significant marker for assessing the risk of thrombotic conditions.