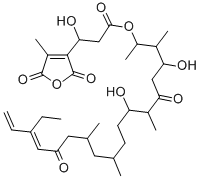
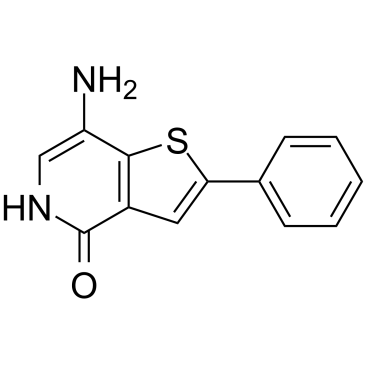
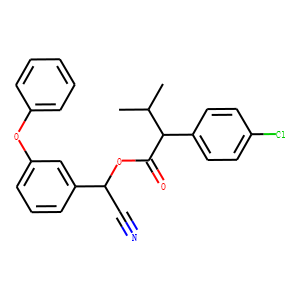
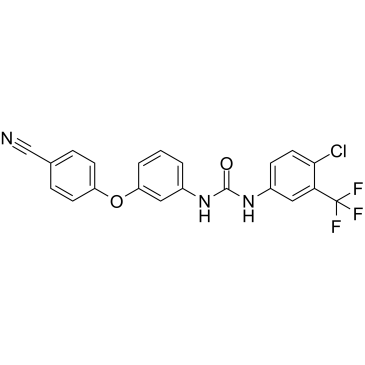
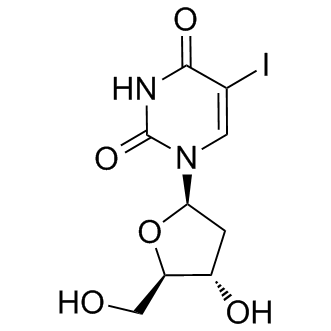
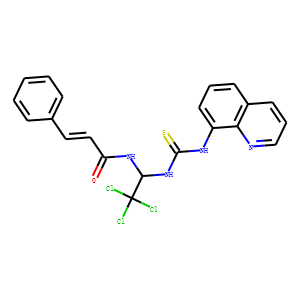
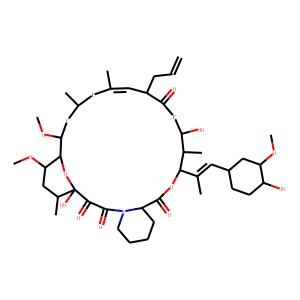
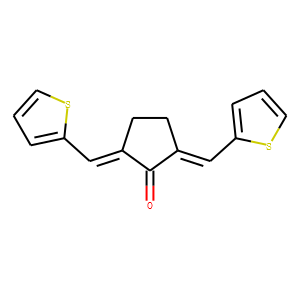
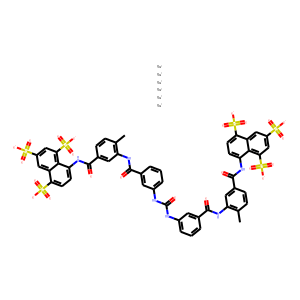
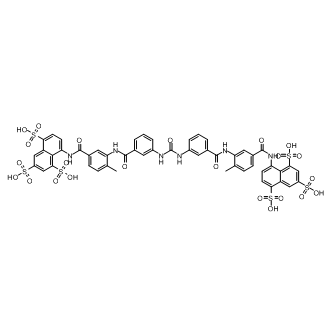
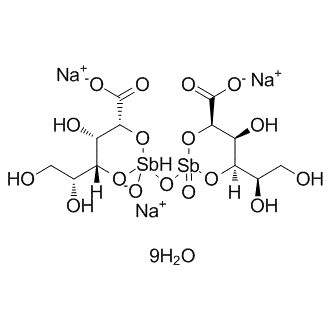
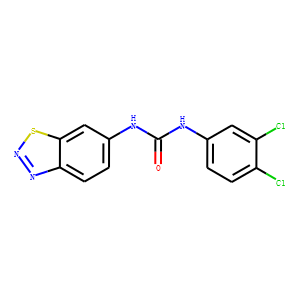
Phosphatase
Phosphatases are enzymes that remove phosphate groups from molecules, a process called dephosphorylation. This action is critical in various cellular processes, including metabolism, signal transduction, and cell cycle control. Phosphatases counterbalance the activity of kinases, which add phosphate groups, thus playing a vital role in maintaining the dynamic balance of phosphorylation in cells. There are two main types: protein phosphatases, which act on proteins, and small molecule phosphatases, which act on other types of molecules. Disruptions in phosphatase activity can lead to diseases such as cancer, diabetes, and neurodegenerative disorders. Research into phosphatase function and regulation continues to be crucial for understanding cellular processes and developing targeted therapies.