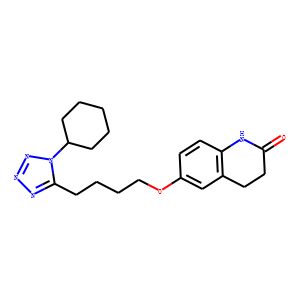
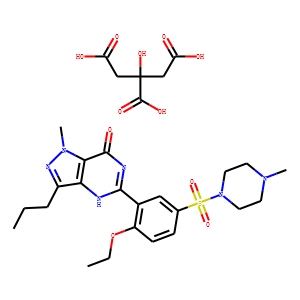
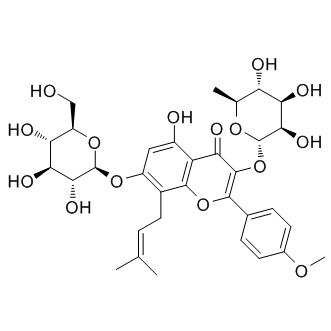
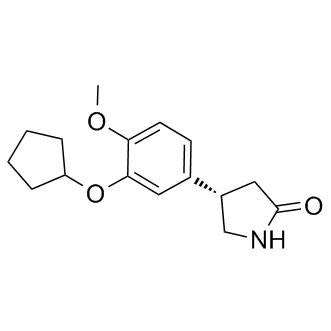
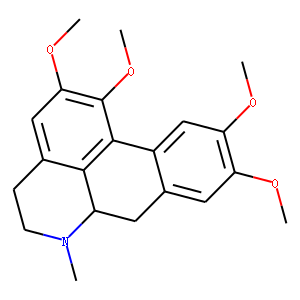
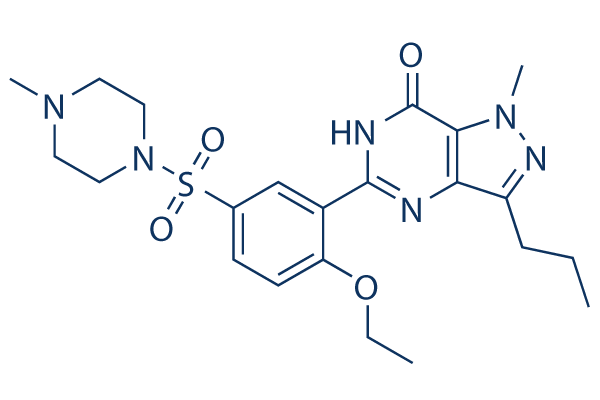
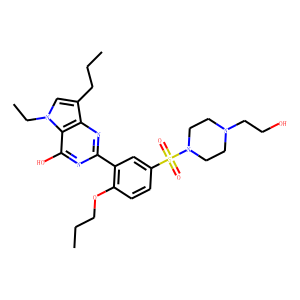
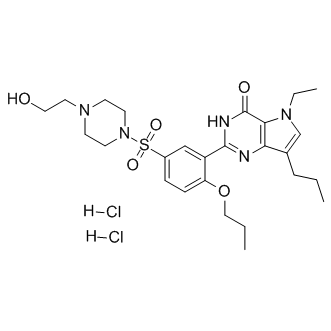
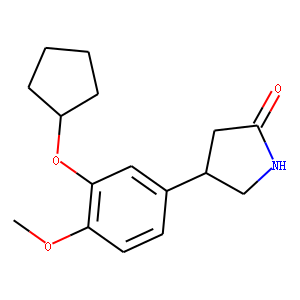
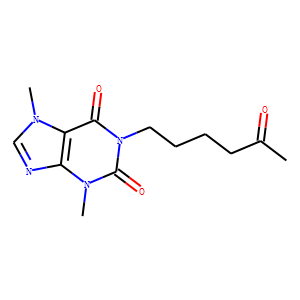
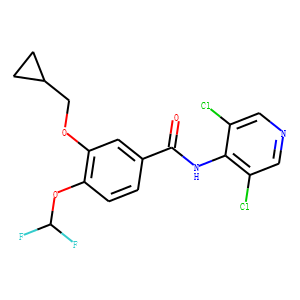
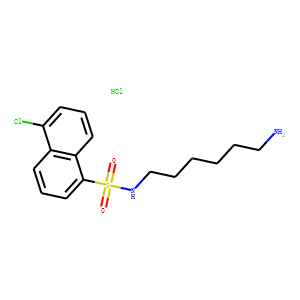
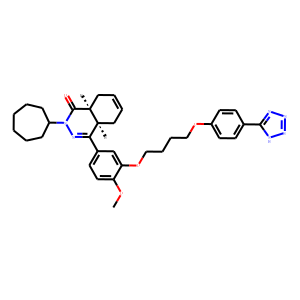
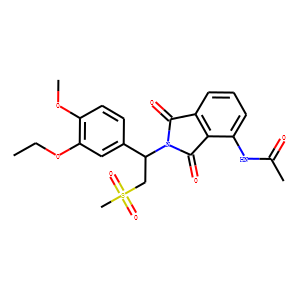
Phosphodiesterase (PDE)
Phosphodiesterases (PDEs) are enzymes that break down the phosphodiester bonds within cyclic nucleotides, such as cyclic AMP (cAMP) and cyclic GMP (cGMP). This action regulates the levels of these signaling molecules, which are crucial for controlling various biological processes including cell division, hormone response, and neuronal function. PDEs are categorized into several families, each with a specific function and tissue distribution, allowing for precise modulation of cellular signaling pathways. Dysfunction in PDE activity can lead to various diseases, such as heart failure, depression, and erectile dysfunction. As a result, PDE inhibitors are important therapeutic agents in treating these conditions by enhancing cAMP or cGMP signaling in target tissues.