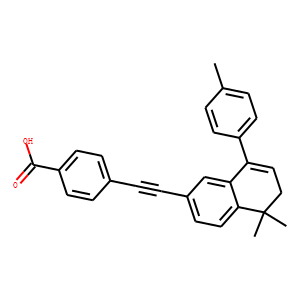
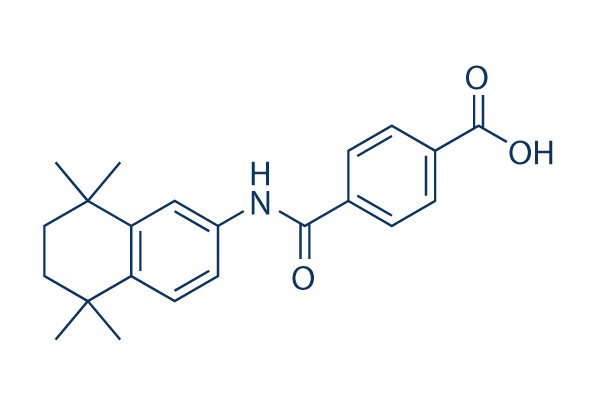
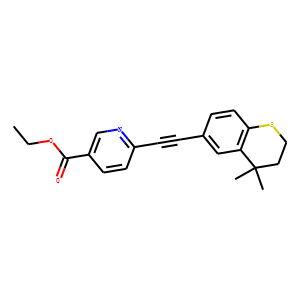
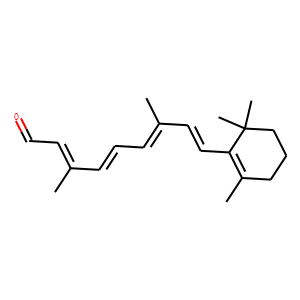
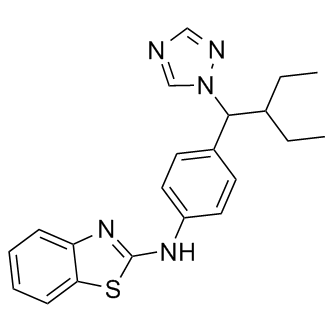
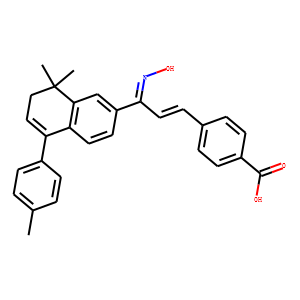
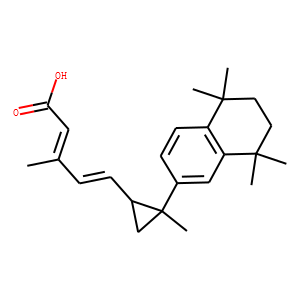
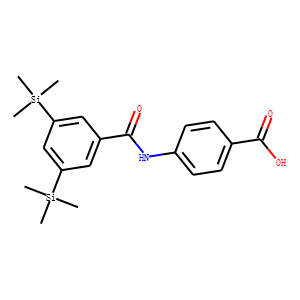
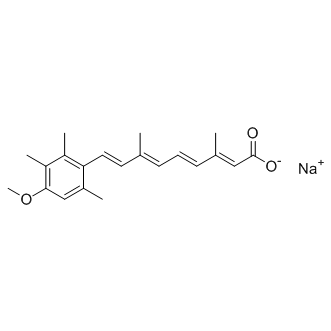
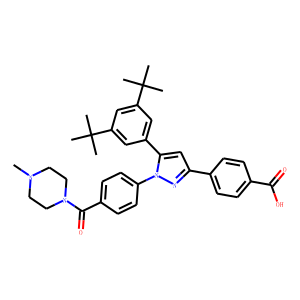
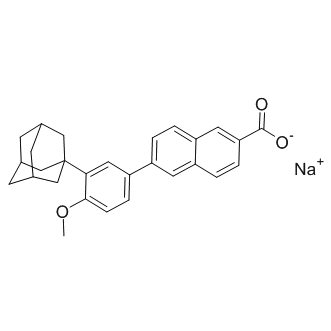
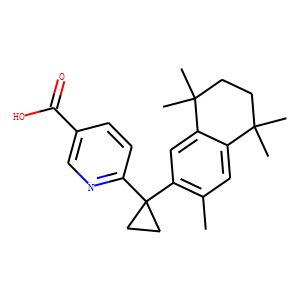
RAR/RXR
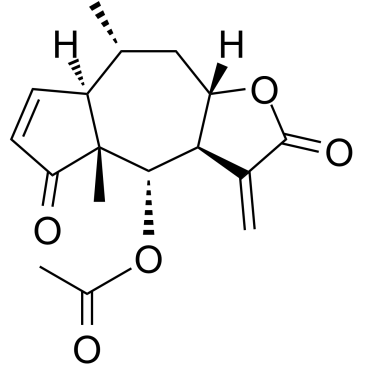
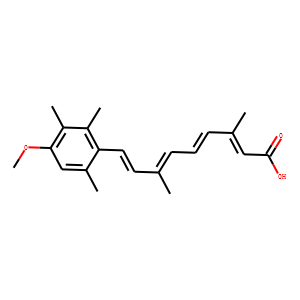
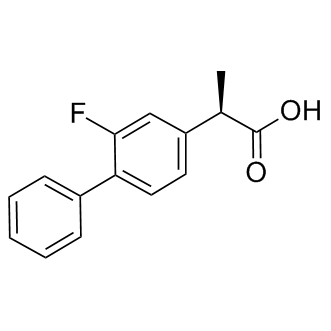
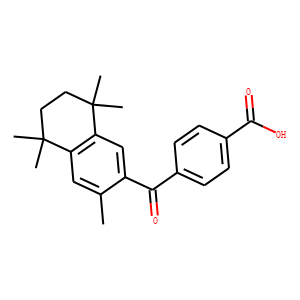
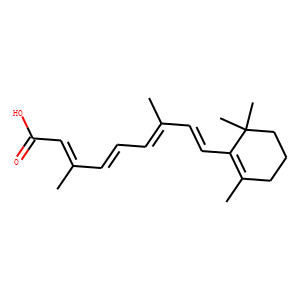
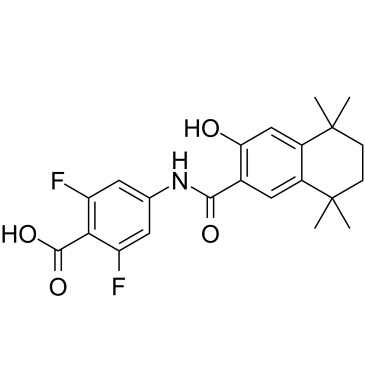
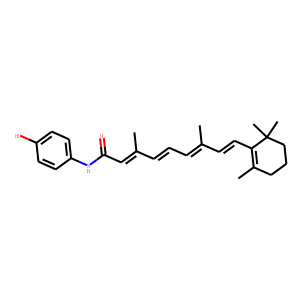
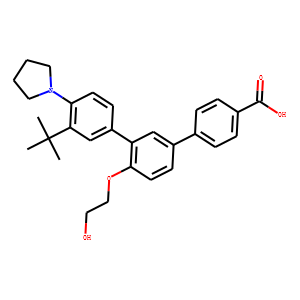
RAR (Retinoic Acid Receptor) and RXR (Retinoid X Receptor) are types of nuclear receptors that mediate the biological effects of retinoids by regulating gene expression. These receptors function as transcription factors that bind to specific DNA sequences in the promoters of target genes. RAR and RXR form heterodimers, which are activated by their ligands—retinoic acids for RAR and 9-cis retinoic acid for RXRs. This activation leads to changes in gene expression that influence processes such as cell differentiation, development, and apoptosis. Dysregulation of RAR and RXR activity is implicated in various diseases, including cancer, making them important targets for therapeutic agents that modulate retinoid signaling pathways.