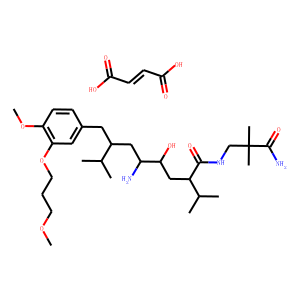
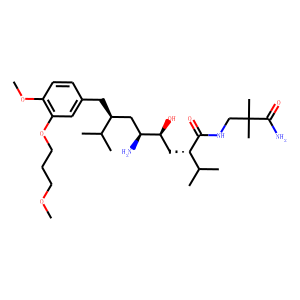
Renin
Renin is an enzyme crucial to the body's regulation of blood pressure, electrolyte balance, and fluid homeostasis. It is primarily produced and released by the kidneys in response to low blood pressure, reduced sodium levels, or sympathetic nervous system activity. Renin cleaves angiotensinogen, a liver-produced protein, into angiotensin I, which is then converted into the potent vasoconstrictor angiotensin II by angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE). Angiotensin II acts to increase blood pressure by constricting blood vessels and stimulating sodium retention and aldosterone release from the adrenal glands. Due to its key role in the renin-angiotensin system, renin is a target for antihypertensive drugs, such as renin inhibitors, which help manage high blood pressure and related cardiovascular conditions.