Tyrosinase
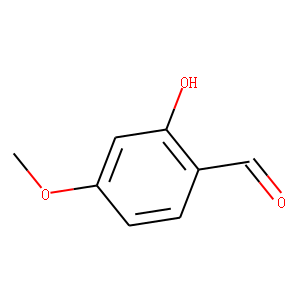
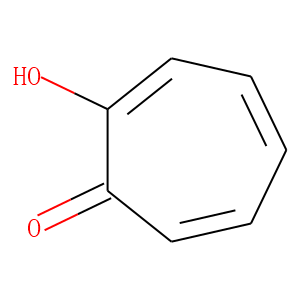
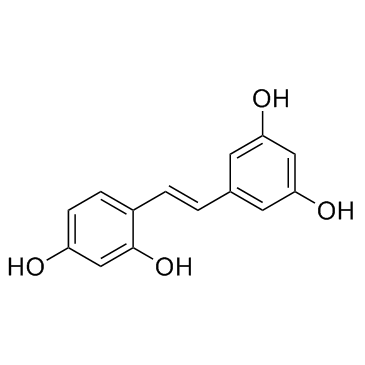
Tyrosinase is a crucial enzyme primarily known for its role in the production of melanin, the pigment responsible for coloring skin, hair, and eyes. It functions by catalyzing the oxidation of tyrosine to DOPA (dihydroxyphenylalanine) and subsequently to dopaquinone, which are steps in the melanin synthesis pathway. Beyond pigmentation, tyrosinase is involved in the browning process in fruits and vegetables and is also significant in wound healing and immune response in some organisms. Structurally, it contains copper ions within its active site, crucial for its enzymatic activity. Tyrosinase's activity can be influenced by various factors including genetic mutations, which can lead to conditions like albinism, characterized by reduced or absent pigment production.