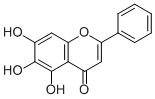
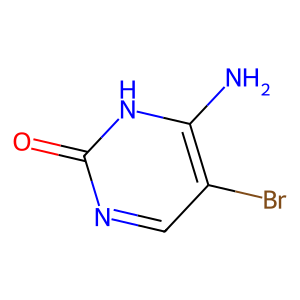
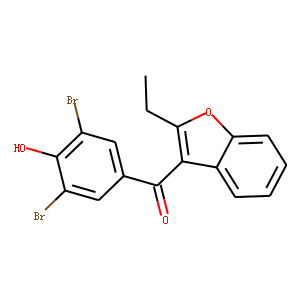
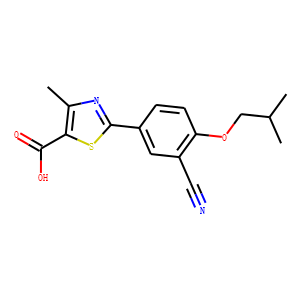
Xanthine Oxidase
Xanthine oxidase is an enzyme that plays a vital role in the catabolism of purines in the body, breaking down nucleotides into uric acid, a waste product excreted in urine. This enzyme catalyzes the oxidation of hypoxanthine to xanthine and then xanthine to uric acid. Xanthine oxidase is found in the liver and intestine, and its activity can be a significant factor in conditions such as gout, where excess uric acid crystallizes in joints causing pain and inflammation. Additionally, it is involved in generating reactive oxygen species, potentially contributing to oxidative stress and cellular damage. Inhibitors of xanthine oxidase, like allopurinol, are commonly used to treat gout and hyperuricemia.