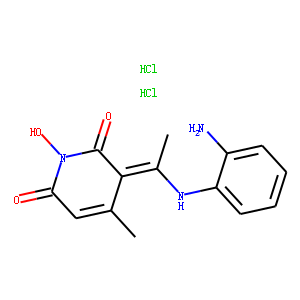
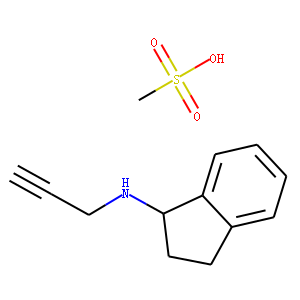
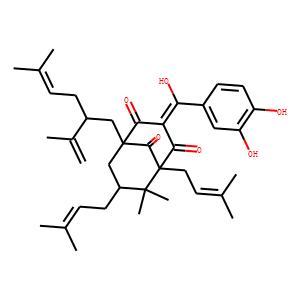
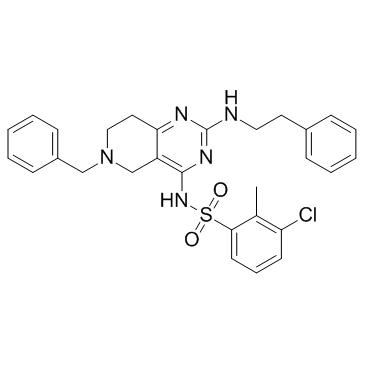
Neuronal Signaling
Neuronal signals are involved in the mechanistic regulation of the CNS(Central nervous system), such as the structure, function, genetics, and physiology of the CNS, and how they can be applied to understand neurological diseases. Each information processing system in the central nervous system is composed of neurons and glial cells, and neurons exhibit unique capabilities in both intracellular signaling and intercellular signaling. G protein-coupled receptors (GPCR), including 5-HT receptors, histamine receptors, and opioid receptors, are the largest class of sensory proteins and are important therapeutic targets for neuronal signaling. Notch signaling in neurons, glial cells, and NSCs(neural stem cells) is also involved in the pathological changes of diseases such as stroke, Alzheimer's disease, and central nervous system tumors. Therefore, targeting neuronal signals, such as Notch signaling and GPCRs, can be used for therapeutic intervention in a variety of different CNS diseases. MuseChem has included small molecule compounds related to neural signaling to facilitate the study of neuromodulation and neurological diseases.