Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)
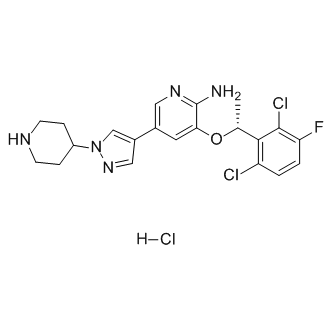
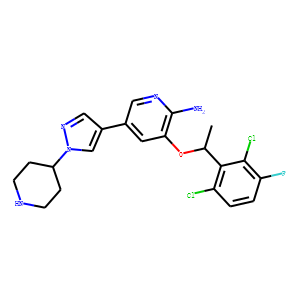
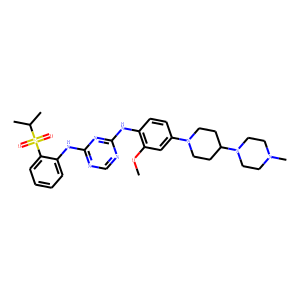
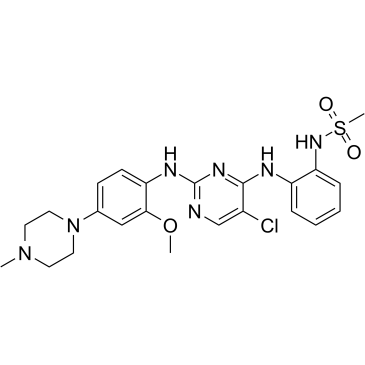
Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) is a receptor tyrosine kinase that plays a key role in the development of the brain and exerts various effects on neuronal differentiation and proliferation. Genetic alterations in ALK, including mutations and translocations, have been identified as oncogenic drivers in several types of cancers, notably non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL), and neuroblastoma. These alterations lead to aberrant activation of ALK signaling pathways, promoting tumor growth and survival. ALK is therefore a significant target for cancer therapy, with several ALK inhibitors, such as crizotinib, developed to specifically inhibit its kinase activity and manage ALK-positive cancers effectively.