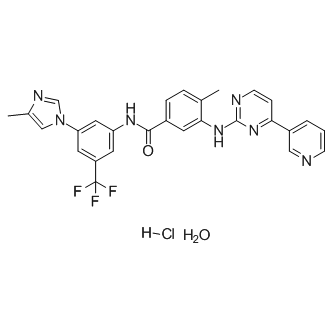
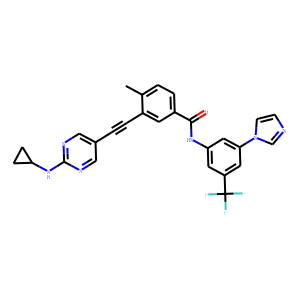
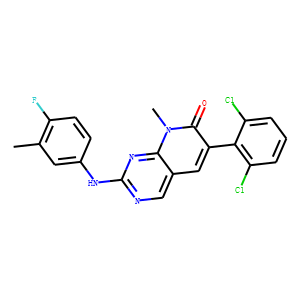
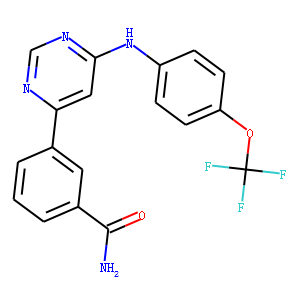
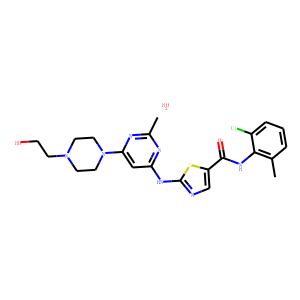
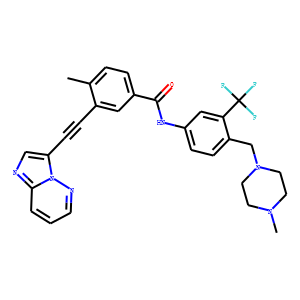
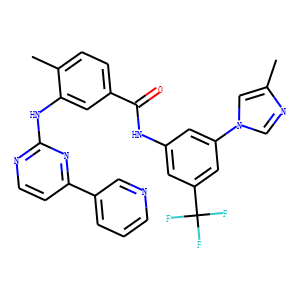
Bcr-Abl
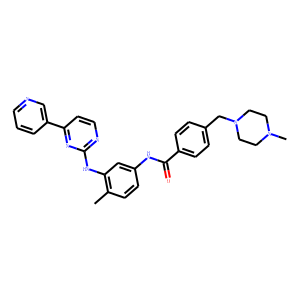
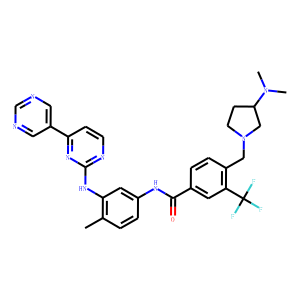
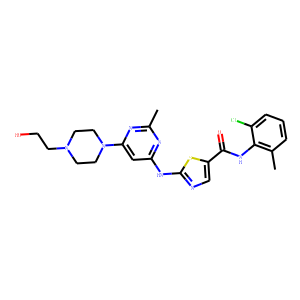
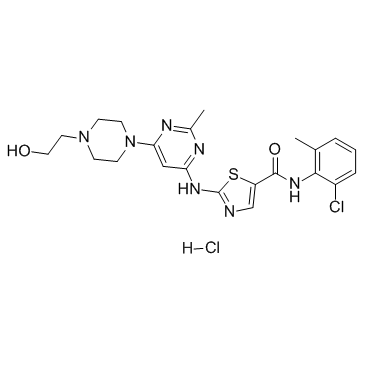
BCR-ABL is an abnormal tyrosine kinase that results from the Philadelphia chromosome translocation, which fuses the BCR gene on chromosome 22 to the ABL gene on chromosome 9. This fusion protein is primarily associated with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) and some forms of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). The presence of BCR-ABL is a hallmark of these diseases, driving cancerous cell proliferation by continuously activating signaling pathways that lead to increased cell division and reduced apoptosis. BCR-ABL is a critical target for targeted cancer therapy, with tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) such as imatinib, dasatinib, and nilotinib proving highly effective in treating CML by specifically inhibiting the kinase activity of BCR-ABL.