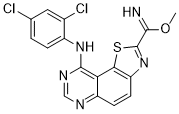
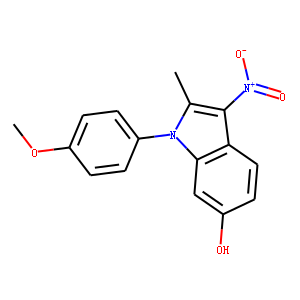
DYRK
DYRK, which stands for Dual-specificity Tyrosine-(Y)-phosphorylation Regulated Kinase, is a family of protein kinases that phosphorylate both serine/threonine and tyrosine residues on substrate proteins. Members of the DYRK family play crucial roles in several cellular processes, including signaling, cell differentiation, and growth. These kinases are particularly important during early developmental stages, influencing neuronal development and function. Dysregulation of DYRK activity has been implicated in a variety of diseases, such as Down syndrome, Alzheimer's disease, and cancer, due to their involvement in cell proliferation and neurobiological processes. As a result, DYRKs are considered potential therapeutic targets, with research focused on developing specific inhibitors to modulate their activity in disease contexts.