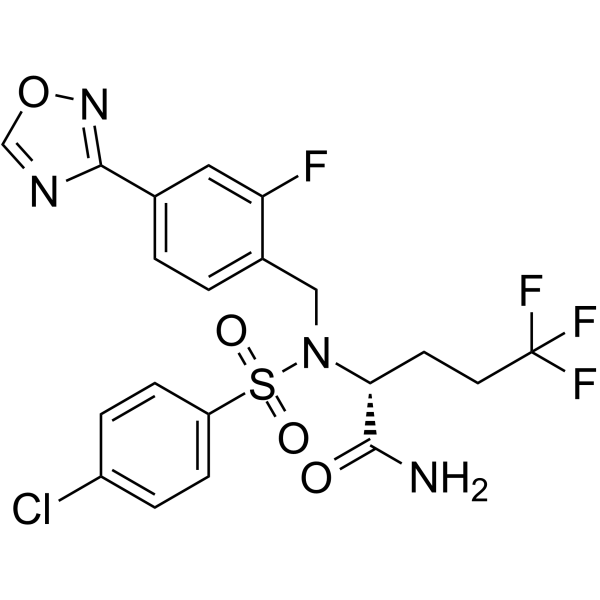
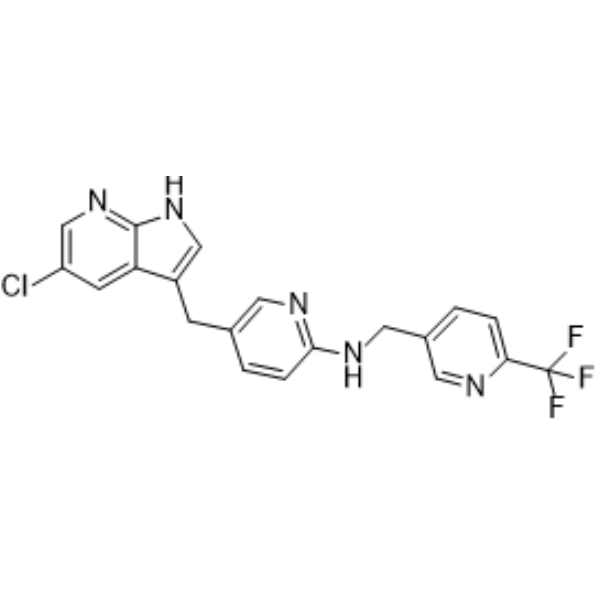
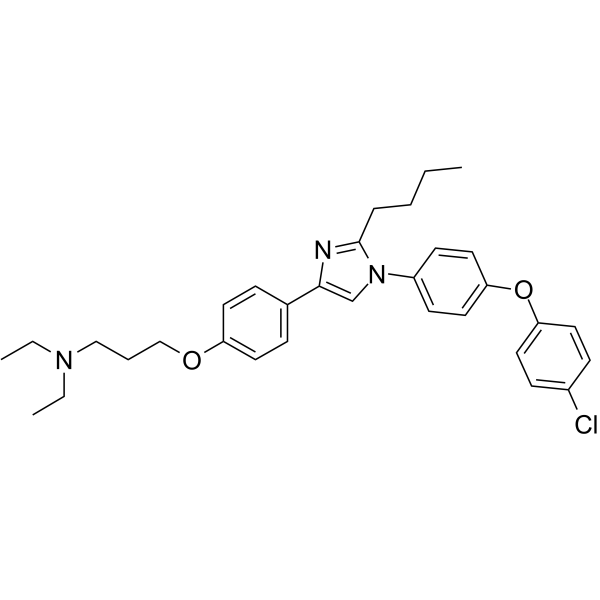
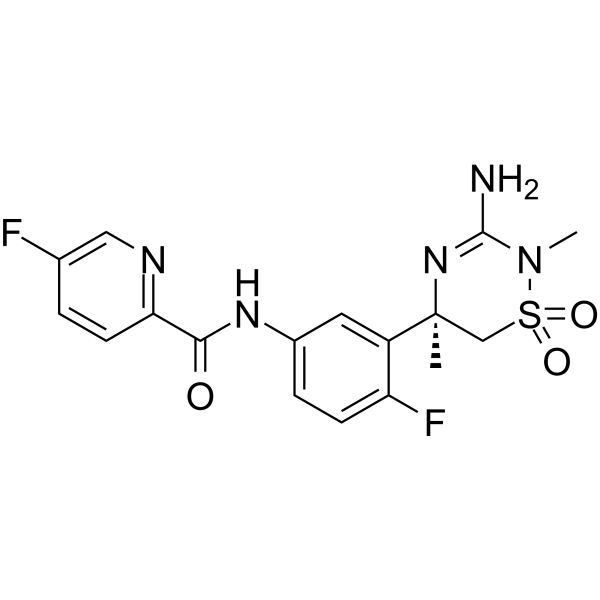
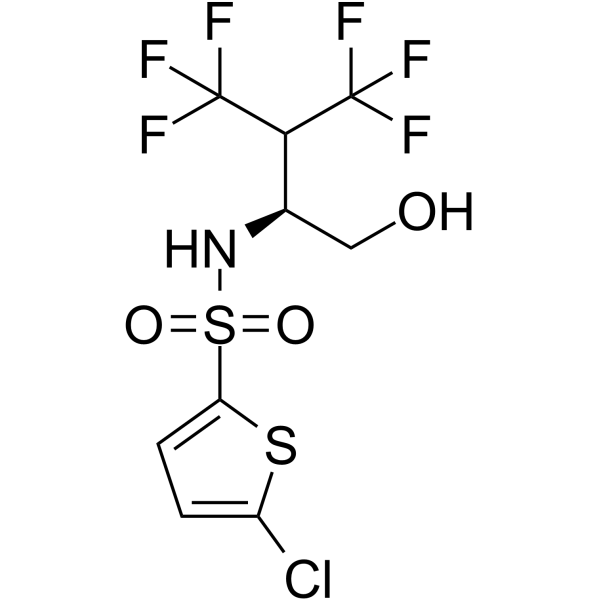
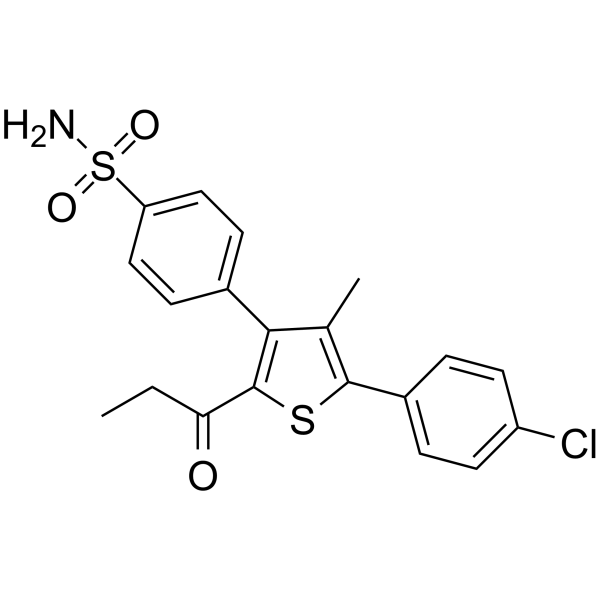
Alzheimer's Disease
Alzheimer's disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder primarily affecting memory, thinking, and behavior. It is the most common cause of dementia, typically manifesting in older adults but can also appear in younger populations. Alzheimer’s disease occurs due to abnormal protein buildups in the brain, specifically amyloid-beta plaques and tau tangles, which damage and kill nerve cells. Symptoms begin with mild memory loss and confusion and can progress to severe cognitive decline, affecting language, judgment, and physical functioning. Risk factors include age, genetics, family history, and lifestyle factors like diet and physical activity. While there is no cure for Alzheimer’s, treatments like cholinesterase inhibitors and NMDA receptor antagonists can manage symptoms. Current research focuses on therapies to slow disease progression, targeting amyloid plaques, tau proteins, inflammation, and neuroprotection. Early diagnosis through cognitive tests, brain imaging, and biomarkers can improve management and quality of life. Alzheimer's remains a major focus in healthcare due to its impact on individuals and families worldwide.