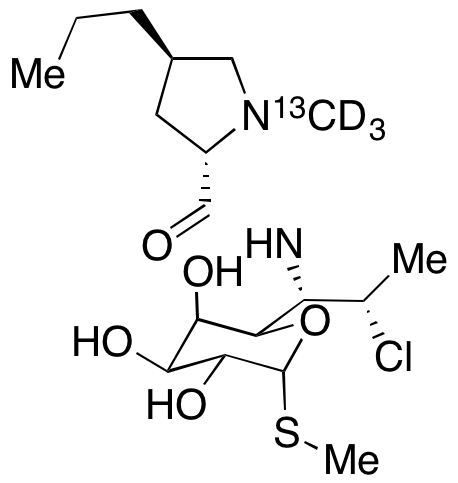
Carbon
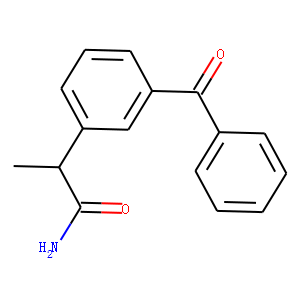
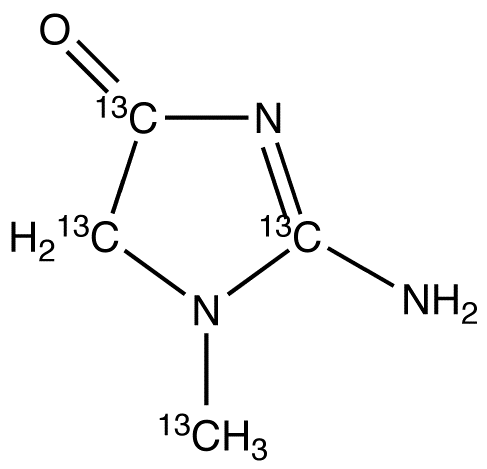
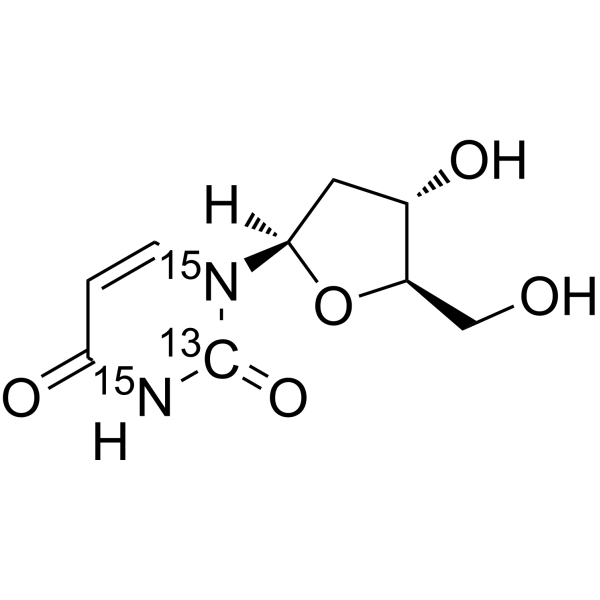
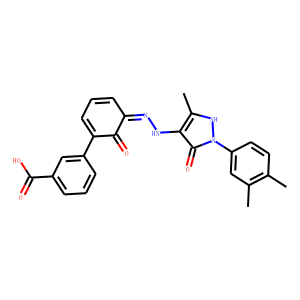
13C and 14C are two isotopes commonly used in isotope labeling. 13C has one extra neutron compared to the more common 12C isotope, while 14C has two extra neutrons. 13C labeling is often used in studies of metabolism and protein structure. By replacing some carbon atoms in a molecule with 13C, researchers can track the fate of those atoms through metabolic pathways or protein interactions using analytical techniques such as nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy or mass spectrometry. 14C labeling is commonly used in radiocarbon dating, where the isotope is used to determine the age of materials up to approximately 50,000 years old. 14C is incorporated into living organisms through carbon dioxide and can be used to track the flow of carbon in the environment. In summary, 13C and 14C labeling compounds are important tools in isotope labeling for tracking the movement of atoms and molecules within a system and for determining the age of materials.