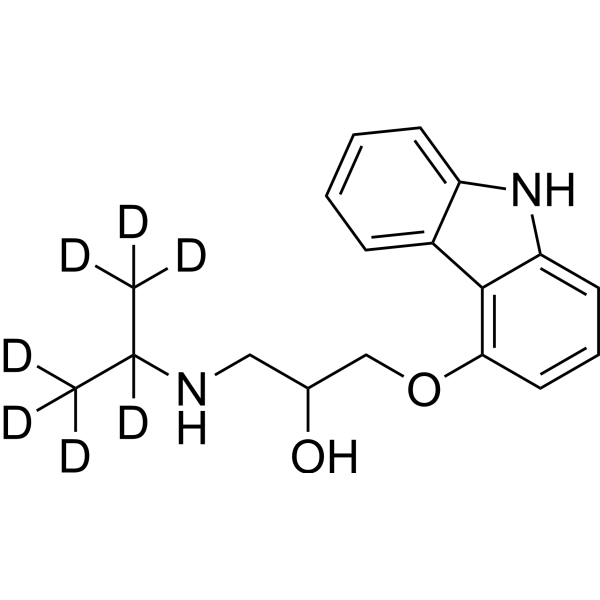
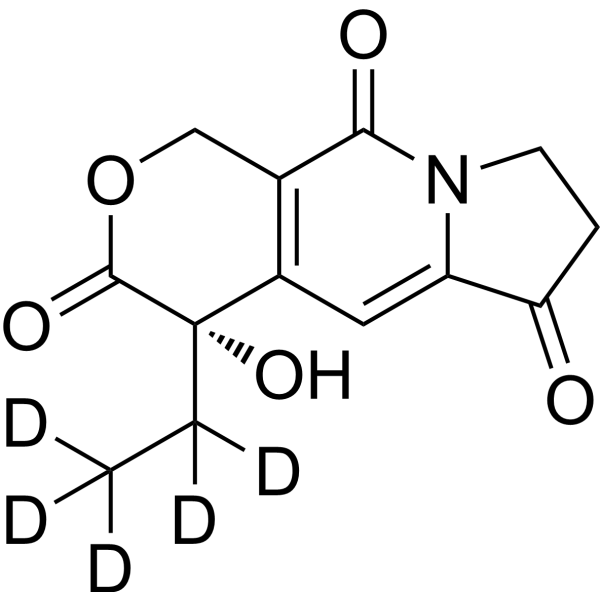
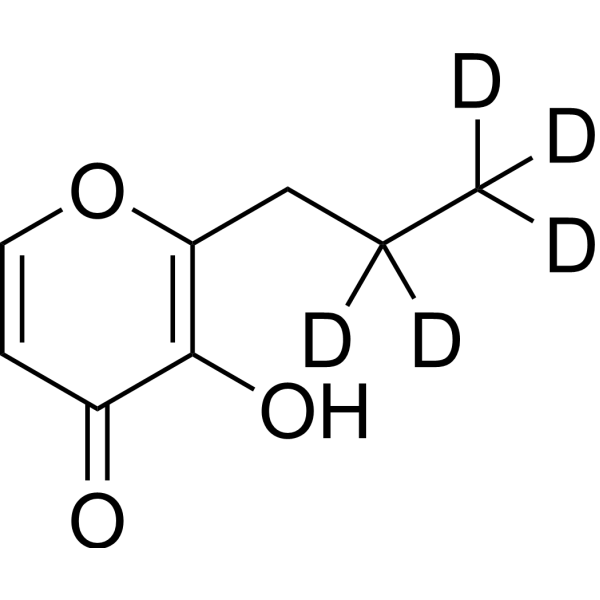
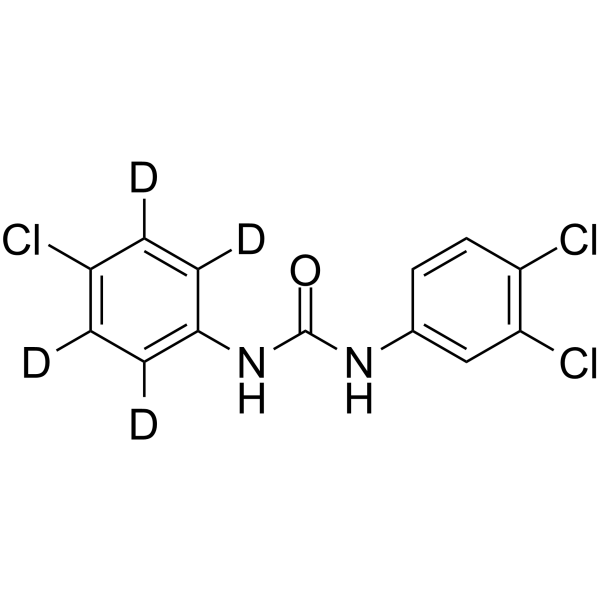
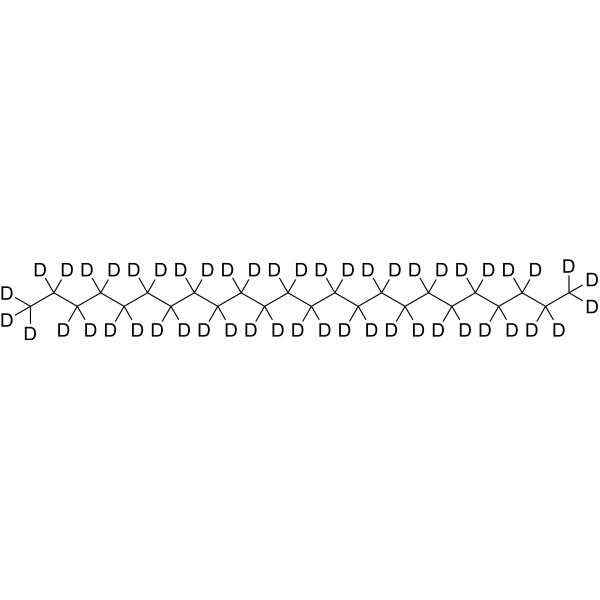Deuterium
Deuterium labeling involves replacing hydrogen atoms in a molecule with deuterium, an isotope of hydrogen with one extra neutron. This technique is often used to study the metabolic fate of molecules in vivo, particularly in lipid, glucose, and amino acid metabolism. Incorporating deuterium into a molecule allows researchers to trace its path through metabolic pathways using mass spectrometry and other analytical techniques. Additionally, deuterium labeling is useful in drug development to study a drug's pharmacokinetics, or how it is absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted by the body. By labeling a drug with deuterium, researchers can track its movement and determine its metabolic fate. In summary, deuterium labeling is a valuable tool in both metabolic studies and drug development. By replacing hydrogen atoms with deuterium, researchers can track the metabolic fate of a molecule or drug, providing insights into biological processes and informing drug design.

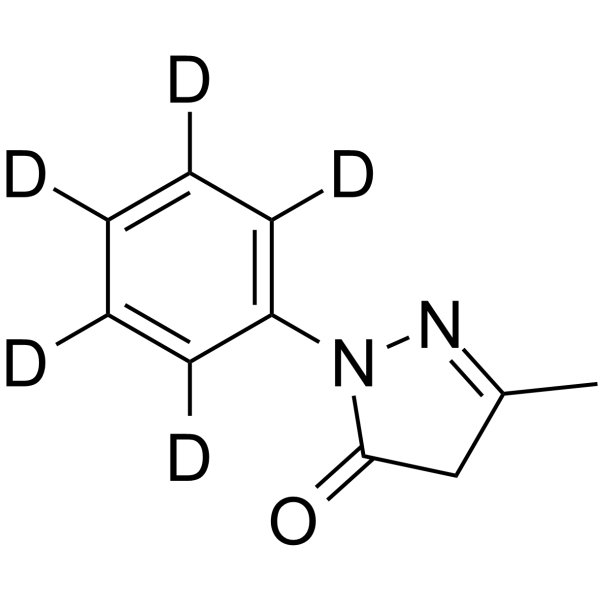
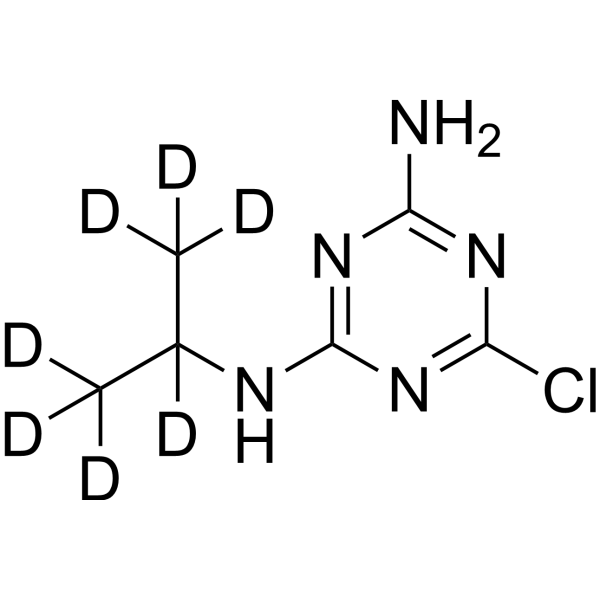
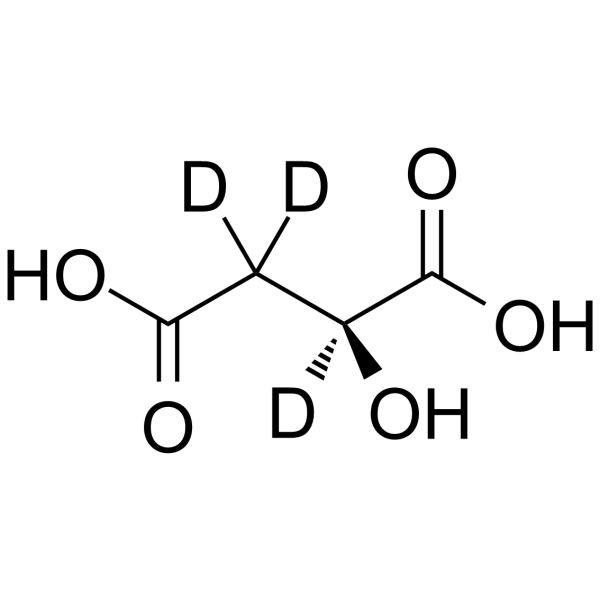
-Neotame-d3.gif)