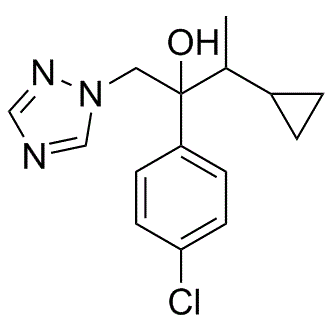
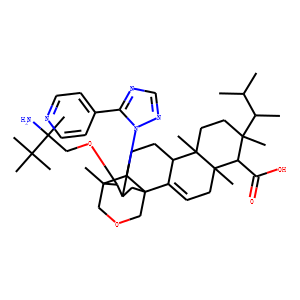
Fungal Infection
Fungal Inhibitors are essential compounds in combating fungal infections by targeting and disrupting critical cellular processes within fungi. These inhibitors work by interfering with cell wall synthesis, membrane integrity, protein synthesis, or enzyme function, thus preventing fungal growth and reproduction. Fungal inhibitors are vital in the treatment of invasive and superficial fungal infections, which can pose serious health risks, especially to immunocompromised individuals. Commonly used in the medical, agricultural, and research fields, fungal inhibitors include classes such as azoles, which disrupt ergosterol synthesis in the cell membrane, and echinocandins, which inhibit glucan synthesis in the cell wall. These inhibitors help manage infections caused by species like Candida, Aspergillus, and Cryptococcus, providing targeted action with reduced toxicity to human cells. High-quality Fungal Inhibitors are integral to developing new antifungal therapies and are widely used in laboratories for studying fungal biology and drug resistance mechanisms.