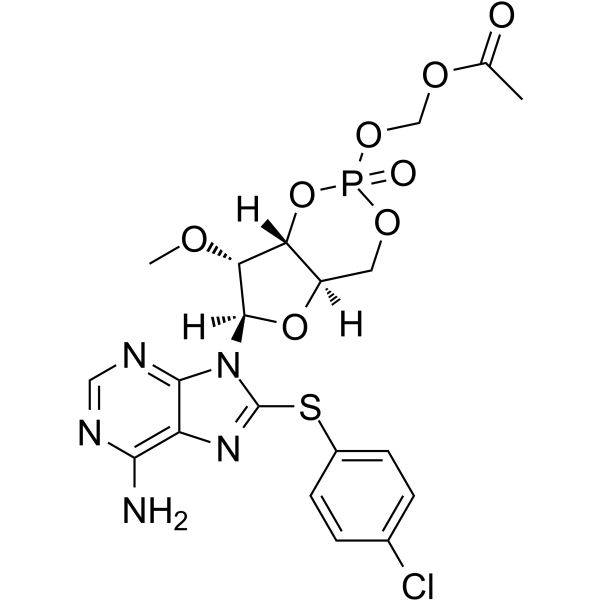
8-pCPT-2′-O-Me-cAMP-AM(Cat No.:I011039)is a synthetic analog of cyclic AMP (cAMP), a critical second messenger involved in intracellular signal transduction. This compound is modified with a 2′-O-methyl group and a p-chlorophenylthio (pCPT) group, enhancing its stability and cellular permeability. The AM (acetoxymethyl) ester form allows for better membrane penetration and hydrolysis inside cells to release active cAMP. 8-pCPT-2′-O-Me-cAMP-AM is used in research to study cAMP-related signaling pathways, including its role in regulating cellular processes such as metabolism, gene expression, and cell proliferation. It serves as a tool in pharmacological and biochemical studies.