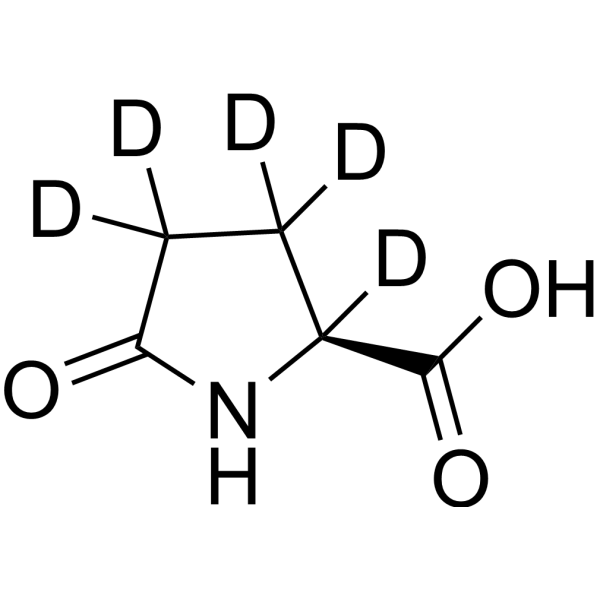
L-Pyroglutamic acid-d5(Cat No.:R040450)is a deuterated form of L-pyroglutamic acid, where five hydrogen atoms are replaced with deuterium, a stable isotope of hydrogen. This modification is commonly used in research to track metabolic pathways involving glutamate metabolism with higher precision using mass spectrometry. L-Pyroglutamic acid-d5 serves as an internal standard in isotope labeling experiments, helping to investigate the role of pyroglutamic acid in various biological processes, such as protein synthesis, neurochemistry, and aging. It is particularly valuable in studying glutamate-related diseases, as well as drug and nutrient metabolism.