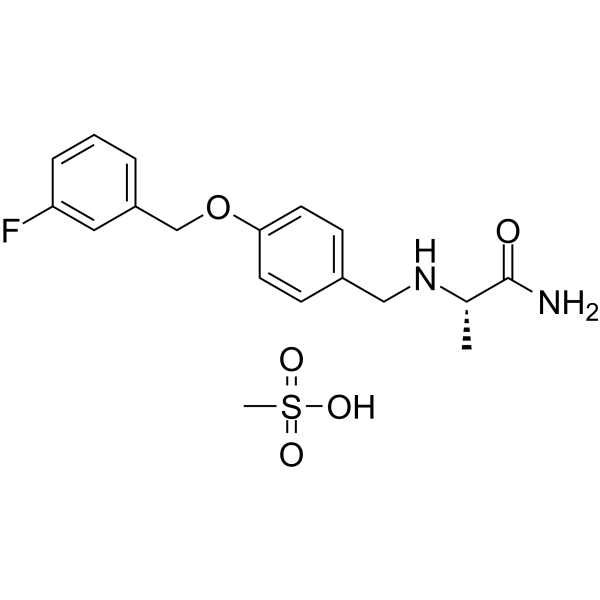
Safinamide mesylate(Cat No.:I009274)is an orally active drug approved for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease as an adjunct to levodopa therapy. It acts as a selective, reversible monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B) inhibitor, enhancing extracellular dopamine levels in the striatum. Beyond MAO-B inhibition, it modulates abnormal glutamate release through sodium channel blockade, contributing to both motor symptom control and potential neuroprotective effects. Safinamide mesylate improves “on” time without troublesome dyskinesia and reduces motor fluctuations. It is also a valuable research tool for studying dopaminergic and glutamatergic pathways in neurodegeneration.