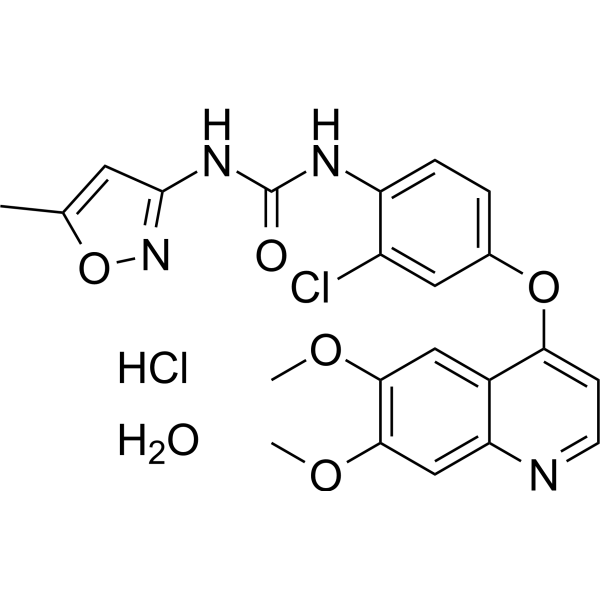
Tivozanib hydrochloride hydrate(Cat No.:I043483)is a potent, oral inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptors 1, 2, and 3, which are critical in tumor angiogenesis. By blocking these receptors, Tivozanib inhibits the formation of blood vessels that supply nutrients to tumors, thus reducing tumor growth and metastasis. It is primarily being studied for the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and other solid tumors. Clinical trials have shown that Tivozanib offers promising efficacy with manageable side effects, positioning it as a potential therapy in cancer treatment. Ongoing research explores its broader applications.